Android - creating custom layout
If it is difficult to gain the desired effect using some standard layout (LinearLayout, GridLayout etc.) or a combination of them, it is relatively easy to programmatically create a custom layout class.
Simply derive from ViewGroup and implement 2 methods: onMeasure() and onLayout().
onMeasure:
- obtains
widthMeasureSpecandheightMeasureSpectelling us what our size should be- these are int variables, but they encode:
- mode:
AT_MOST,EXACTLY,UNSPECIFIED(useMeasureSpec.getMode()to extract mode) — the obtained mode depends on thelayout_width/layout_heightattributes (wrap_contentisAT_MOST;match_parent(=fill_parent) or a specific size isEXACTLY) - size: a number specifying size (use
MeasureSpec.getSize()to extract size)
- mode:
- these are int variables, but they encode:
- we have to calculate our dimensions and set them using
setMeasuredDimension()at the end - our dimensions depend on the input
measureSpecvalues and on the size of our children - so, iterate the children (using
getChildCount()andgetChildAt()):- prepare
MeasureSpecfor each child (usingMeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec()) and callchild.measure()) - obtain measured dimensions from each child using
child.getMeasuredWidth()andchild.getMeasuredHeight()
- prepare
onLayout:
- we have to set the absolute position of each child by calling
child.layout() - we can use the dimensions of the children measured previously (by calling
child.getMeasuredWidth()andchild.getMeasuredHeight()) - we can use our measured dimensions (by calling
getMeasuredWidth()andgetMeasuredHeight())
Example 1: Flow layout
This layout lays out the children like letters in a text — it tries to fill each row and if it is not possible, it continues on the next row.
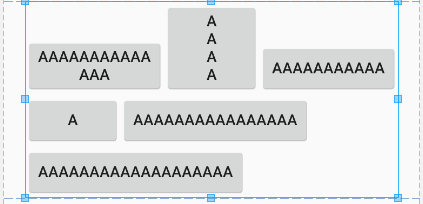
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int childWidthMeasureSpec = 0;
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = 0;
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
int totalWidth = 0;
int totalHeight = 0;
int currentLineWidth = 0;
int currentLineHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean fitsToCurrentLine = (currentLineWidth == 0) || (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) || (currentLineWidth + childWidth <= MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec));
if (!fitsToCurrentLine) {
totalWidth = Math.max(totalWidth, currentLineWidth);
totalHeight += currentLineHeight;
currentLineWidth = 0;
currentLineHeight = 0;
}
currentLineWidth += childWidth;
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childHeight);
}
totalWidth = Math.max(totalWidth, currentLineWidth);
totalHeight += currentLineHeight;
setMeasuredDimension(
fixFinalDimension(totalWidth, widthMeasureSpec),
fixFinalDimension(totalHeight, heightMeasureSpec)
);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int totalWidth = 0;
int totalHeight = 0;
int currentLineWidth = 0;
int currentLineHeight = 0;
int currentLineFirstIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean fitsToCurrentLine = (currentLineWidth == 0) || (currentLineWidth + childWidth <= getMeasuredWidth());
if (!fitsToCurrentLine) {
layoutOneLine(currentLineFirstIndex, i - 1, currentLineHeight, totalHeight);
totalWidth = Math.max(totalWidth, currentLineWidth);
totalHeight += currentLineHeight;
currentLineWidth = 0;
currentLineHeight = 0;
currentLineFirstIndex = i;
}
currentLineWidth += childWidth;
currentLineHeight = Math.max(currentLineHeight, childHeight);
}
layoutOneLine(currentLineFirstIndex, childCount - 1, currentLineHeight, totalHeight);
}
private void layoutOneLine(int currentLineFirstIndex, int currentLineLastIndex, int lineHeight, int lineY) {
int currentX = 0;
for (int i = currentLineFirstIndex; i <= currentLineLastIndex; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(currentX, lineY + lineHeight - childHeight, currentX + childWidth, lineY + lineHeight);
currentX += childWidth;
}
}
private int fixFinalDimension(int calculatedDimension, int measureSpec) {
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec) == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
if (calculatedDimension > MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)) {
return MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
}
}
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
if (calculatedDimension != MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)) {
return MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
}
}
return calculatedDimension;
}
}Example 2: Equal size layout
This layout lays out the children in a row and ensures that all children have minimal possible, but the same dimensions.
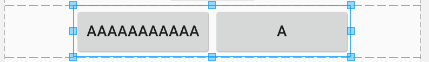
public class EqualSizeLayout extends ViewGroup {
public EqualSizeLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public EqualSizeLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int maxChildWidth = 0;
int maxChildHeight = 0;
int childWidthMeasureSpec = 0;
if (childCount > 0) {
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) / childCount, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) / childCount, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
}
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
maxChildWidth = Math.max(maxChildWidth, childWidth);
maxChildHeight = Math.max(maxChildHeight, childHeight);
}
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(maxChildWidth, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY), MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(maxChildHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
}
setMeasuredDimension(
fixFinalDimension(maxChildWidth * childCount, widthMeasureSpec),
fixFinalDimension(maxChildHeight, heightMeasureSpec)
);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int currentX = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(currentX, 0, currentX + childWidth, childHeight);
currentX +=childWidth;
}
}
private int fixFinalDimension(int calculatedDimension, int measureSpec) {
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec) == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
if (calculatedDimension > MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)) {
return MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
}
}
if (MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
if (calculatedDimension != MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)) {
return MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
}
}
return calculatedDimension;
}
}Testing
When implementing a custom layout in Android Studio, we can test it directly in the GUI preview (in the Design view of some layout XML file) — we have not to execute the application on the device or an emulator. Android Studio always executes our layout code to prepare the preview. Only a rebuild of the code after making a change in the layout code is needed.
Watch corner cases: it can always happen that the view has 0 children or the width/height of the view or some child is 0. Test these corner cases — it is very easy to forget about it and encounter some division be zero during the calculations.
To ensure that we follow the desired measureSpec given to us in onMeasure(), we call fixFinalDimension() to correct the dimensions we are going to return. Imagine that we have some bug in our calculations or that some child does not follow the measureSpec from us and returns arbitrary size instead. This would cause returning dimensions that do not match the measureSpec. We do not want to propagate any invalid dimensions to our parent and cause broken layouts even outside our view.
Performance
Our custom onMeasure() and onLayout() methods can be called quite frequently — imagine moving an application boundary in Android 7 split screen view — the application has to re-layout on every single step during the moving. So, the layout code has to be as fast as possible.
Some caching can be used if something calculated in onMeasure() can be reused in onLayout() — e.g. our FlowLayout has almost identical code in onMeasure() and onLayout() — it should simply remember the calculated positions of children and reuse them in onLayout().
Avoid using objects. Use only primitive types. This avoids garbage collections of many objects created during many relayouts. Note that the measureSpec variables follow this idea — they encode both mode and size in one primitive type.
Features missing in the examples
Child visibility
The calculations in both onMeasure() and onLayout() should watch the visibility of the child (using child.getVisibility()) — if the visibility is GONE, do not take the child size into account.
Padding
The padding of our layout (set e.g. using android:padding) should be considered in calculations in onMeasure() and onLayout(). Simply get the padding set up on each side (e.g. using getPaddingLeft()) and include it in the calculations.
LayoutParams
We could implement a custom class derived from LayoutParams. LayoutParams objects could be set to children of our layout and so each child could have some properties set up which our layout calculations can read and follow — for example position on line or behavior if the child width wants to exceeds the line width in FlowLayout. We can use LayoutParams class directly — it already has 2 useful members: width and height (they can have specific size set up or special values of match_parent (= fill_parent) or wrap_content).