Jenkins - alternative way of uploading a web site to a FTP server
Jenkins, with FTP publisher plugin, provides the Publish artifacts to FTP post-build action. Here, I will show another way how to accomplish uploading to FTP - using LFTP.
Configure main Jenkins project
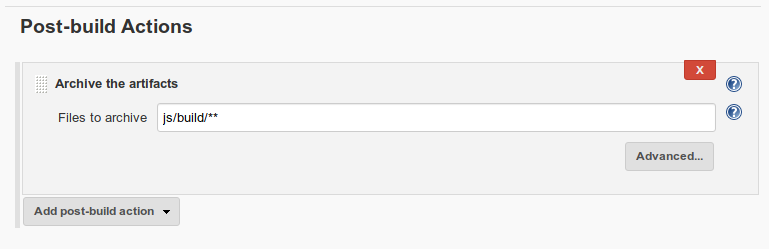
Make sure the Jenkins project which actually builds the web site correctly archives the output artifacts:
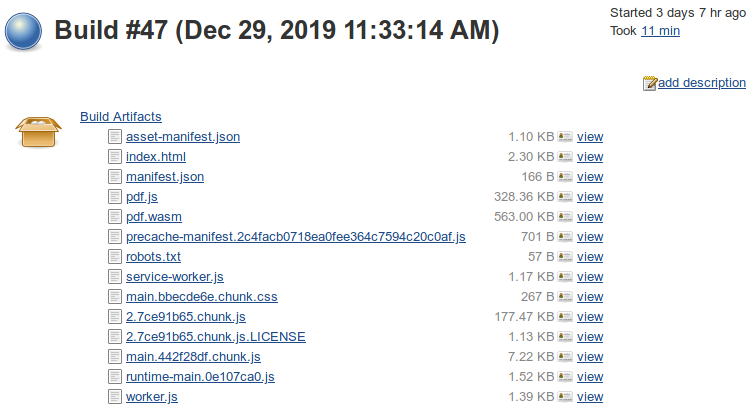
Run it to see that the artifacts have been archived successfully:
Create a separate publishing Jenkins project
This project will run independently of the main project - it will be executed manually, only when the publishing is needed.
It fist prepares files to be uploaded - collects (copies) them to its own workspace which will serve as an intermediate directory before the upload happens.
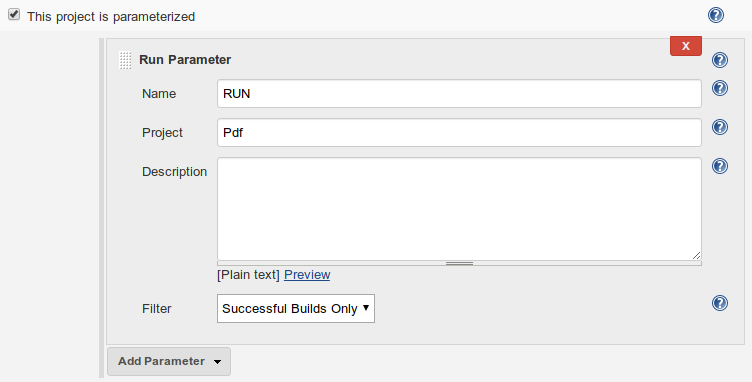
Add a Run Parameter pointing to the main project. This parameter will provide a selection from the main project runs, so we will be able to choose a specific run to take the artifacts from.
Add an Execute shell build step:
set -e
set -x
set -u
rsync --verbose --checksum --delete --recursive $JENKINS_HOME/jobs/<main_job_name>/builds/$RUN_NUMBER/archive/<path_to_built_files>/ .
HOST='<some.ftp.server>'
USER='<some_ftp_user>'
PASSWORD='<password>'
SOURCEDIR='.' # we will upload the whole project workspace
TARGETDIR='<target_dir>'
lftp -f "
open $HOST
user $USER $PASSWORD
mirror --reverse --delete --verbose -x <excluded> $SOURCEDIR $TARGETDIR
bye
"Use rsync to copy archived artifacts from the main project to the workspace of this project.
- The
RUN_NUMBERvariable is provided by theRun Parameterwe specified earlier. - The interesting files can be in some sub-directory, so take care to add a correct
path_to_built_filespart. - The
--checksumargument is part of our effort to upload only files which were really changed since the last upload. This argument ensures thatrsynccompares each file by its contents to ensure that the file is not copied if a file with exactly the same contents already exists in the target directory (workspace of this project) - the already existing file will stay there with the same modification time set as before. This is important becauselftpwill use this time to check whether to re-upload the file. Here, we take advantage of the fact that we can easily compare the whole files by their contents (not taking shortcuts and compare only modification time or file size), because they reside on our disk. - For the same reason, make sure
Delete workspace before build startssetting is unchecked.
Use lftp to upload the files to the server:
- We can upload to some sub-directory on the server by specifying
target_dir - Use
set ftp:ssl-allow no;before theopencommand if there are problems with the secure communication (make sure you understand the consequences). - Specify files or directories on the server which you do not want to be touched by the synchronization process in
excluded. E.g..htaccessto ignore any .htaccess file already residing on the server or^upload/to ignore the upload directory. - Note: Password can be protected by using the
Credentialsfeature of Jenkins, so that it will not be printed to the console output.
Test the publishing
Choose Build with Parameters and select the run to take artifacts from:

The rsync output will tell us about the files which were really changed:
sending incremental file list
deleting precache-manifest.869aeef97b53a77a11eaaee1bc041d63.js
deleting static/js/runtime-main.776538eb.js
deleting static/js/main.dbedf050.chunk.js
asset-manifest.json
index.html
precache-manifest.3069d95ed8ea54fd071bbd01f4e2ec80.js
service-worker.js
static/js/main.46d1c7ff.chunk.js
static/js/runtime-main.0e107ca0.js
sent 10,069 bytes received 264 bytes 20,666.00 bytes/sec
total size is 1,061,096 speedup is 102.69The lftp output will show that only the changed files were uploaded:
source: Is a directory
Removing old file `asset-manifest.json'
Transferring file `asset-manifest.json'
Removing old file `index.html'
Transferring file `index.html'
Transferring file `precache-manifest.3069d95ed8ea54fd071bbd01f4e2ec80.js'
Removing old file `service-worker.js'
Transferring file `service-worker.js'
Transferring file `static/js/main.46d1c7ff.chunk.js'
Transferring file `static/js/runtime-main.0e107ca0.js'
Removing old file `static/js/main.dbedf050.chunk.js'
Removing old file `static/js/runtime-main.776538eb.js'
Removing old file `precache-manifest.869aeef97b53a77a11eaaee1bc041d63.js'Advantages of this approach
- The main project and publishing project run independently. The main project can run e.g. after any source code change. We can run the publishing project manually after e.g. testing the artifacts of a specific run of the main project and deciding that we really want to publish these artifacts.
- LFTP provides a lot of options, it even includes the exclude option to ignore some files or directories on the server.
- We can upload only files which were really changed, which helps with slow connections or slow servers.
Other notes
- Such project structure (some project using artifacts from other project) can be used for other scenarios (not only publishing) - in a separate project, we can e.g. run some automated tests over the archived artifacts. The test project can then fail independently of the main project and we can re-run the tests without the need to build the main project again.